Search Results for: white substance
White substance
white substance --> white matter (Science: anatomy) brain tissue composed of myelin-coated nerve cell fibres. White... Read More
Nervous System
THE is the most complicated and highly organized of the various systems which make up the human body. It is the... Read More
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis Definition Phagocytosis is a basic physiological cellular process wherein a cell ingests a solid particle... Read More
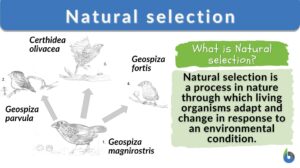
Natural selection
Natural Selection Definition What is natural selection in biology? Natural selection is defined as a process in nature... Read More
Unconditioned stimulus
An unconditioned stimulus inherently triggers an automatic response, not reliant on deliberate prior learning. In contrast... Read More
Chlorophyll
Why are most plants green? Have you ever had the same question? Perhaps, you’ve been told that the plants are green... Read More
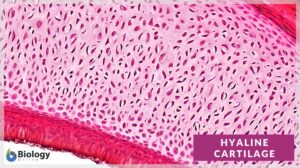
Hyaline cartilage
Hyaline Cartilage Definition Before we define hyaline cartilage, let us understand what cartilage is. What is cartilage? Is... Read More
Endocytosis
Endocytosis Definition What is endocytosis in biology? Endocytosis is a cellular process by which a cell internalizes any... Read More
Pathobiology of allergy and its most severe form, anaphylaxis
When allergy season looms, some people with serious hypersensitivity to allergens tend to be apprehensive of what may come.... Read More
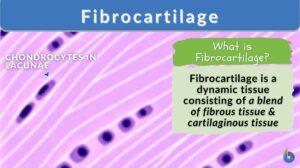
Fibrocartilage
What Is Fibrocartilage? Fibrocartilage is the strongest transitional connective tissue made up of collagen fibers and... Read More
Spongy bone
Spongy bone, also known as cancellous bone or trabecular bone, is a type of bone tissue found at the ends of long bones and... Read More
Dense connective tissue
Definition noun A type of connective tissue that contains chiefly of collagen fibers (type I collagen) relative to the... Read More
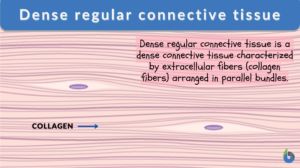
Dense regular connective tissue
The dense connective tissue is a type of connective tissue proper that consists predominantly of fibers, especially type I... Read More
Achromatic
Achromatic (Science: microscopy) Literally, colour-free. A lens or prism is said to be achromatic when corrected for two... Read More
Saturation
saturation 1. The act of saturating, or the state of being saturating; complete penetration or impregnation. 2. (Science:... Read More
Characteristic
Characteristics Definition We can define characteristics as qualities or features that describe the distinctive nature or... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Examples of Natural Selection
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D.Darwin's Finches Darwin's finches are an excellent example of the way in... Read More
Myocardium
Myocardium Definition What is the myocardium of the heart? It is the muscular middle layer of the heart that is... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More